To understand diamond clarity, we must first understand how diamonds are created. Natural diamonds are the result of carbon exposed to tremendous heat and pressure deep in the earth. This process can result in a variety of internal characteristics called ‘inclusions’ and external characteristics called ‘blemishes.’
Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. If you are trying to determine what is the best clarity for a diamond, remember that no diamond is perfectly pure. But the closer it comes to purity, the better its clarity.
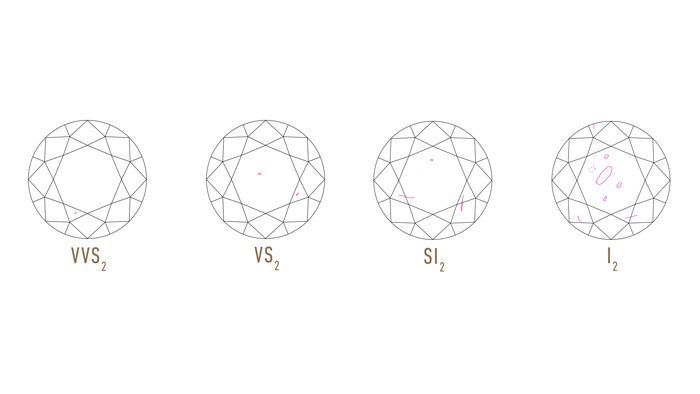
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades.
- Flawless (FL) No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification
- Internally Flawless (IF) No inclusions visible under 10x magnification
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification
- Included (I1, I2, and I3) Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
Many inclusions and blemishes are too tiny to be seen by anyone other than a trained diamond grader. To the naked eye, a VS1 and an SI2 diamond may look exactly the same, but these diamonds are quite different in terms of overall quality. This is why expert and accurate assessment of diamond clarity is extremely important. Knowing what diamond clarity truly means helps you understand the factors that contribute to diamond quality and price.